SNE Master Research Projects 2012 - 2013

|
2004- 2005 |
2005- 2006 |
2006- 2007 |
2007- 2008 |
2008- 2009 |
2009- 2010 |
2010- 2011 |
2011- 2012 |
2012- 2013 |
2013- 2014 |
2014- 2015 |
2015- 2016 |
2016- 2017 |
2017- 2018 |
2018- 2019 |
2019- 2020 |
2020- 2021 |
2021- 2022 |
| Contact | TimeLine | Projects | LeftOver Projects | Presentations-rp1 | Presentations-rp2 | Objective | Process | Tips | Project Proposal |
Contact
Cees de Laat
tel: +31205257590 room: C.3.152 |
|
TimeLine
RP1:
|
RP2:
|
ProjectsHere is a list of student projects. Find here the left over projects this year: LeftOvers.In a futile lightweight way to prevent spam I replaced "@" by "=>" in the table. Color of cell background:
|

|
| # | title summary |
supervisor contact students |
R P |
1 / 2 |
| 3 SN |
Traffic Volume vs. Network Inspection.Traffic volume remains ever-increasing. Peak throughput at AMSIX for example saw a yearly increase from 0.8T to 1.2T roughly (sep 2010 vs. sep 2011). Yet simultaneously growing needs to deal with increasingly evasive network applications, increasingly strenuous compliance regulations, and high-profile malware activity (Mariposa, Conficker, STUXnet, …) has given rise to powerful real-time inspection technology.An important question is if it is possible, and if so how, to bring and keep inspection capacity close to full network capacity, even in the face of continuous strong growth. |
Jeroen Scheerder <Jeroen.Scheerder=>on2it.net> Fahimeh Alizadeh <Fahimeh.Alizadeh=>os3.nl> Rawi Ramdhan <rawi.ramdhan=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 4 SN |
Linux Open Source Distributed Filesystem. Type: Research, prototyping, file system technology, storage Required time: 4 weeks for 1 SNE student; Company: SURFsara, URL: http://www.surfsara.nl SURFsara would like to research the use of a Linux open source distributed file system for a large and scalable on-disk data archive. Key points of interest are scalability, reliability, and ease of maintenance. Possible candidates for such a distributed filesystem are:
The student will get full access to our testbed environment, consisting of one rack of Linux disk storage servers. Required skills: Linux system administration from the command-line. Required knowledge: UNIX operating systems. Knowledge about filesystems and clustering are preferred. |
Walter de Jong <walter.dejong=>surfsara.nl> Remco van Vugt <remco.vanvugt=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 8 N |
FileSender Terabyte Challenge.The FileSender project (www.filesender.org) issues the Terabyte Challenge. Current upload speeds with FileSender are nice for files up to several GBs. We want to enable use of FileSender to transfer a 1 TB file in a reasonable amount of time (5 hours on a low latency path) using a standard web browser on a standard Windows or Mac desktop. Identify current performance bottlenecks and design possible solution strategies which hold as latency increases.Work can be conducted in Norway or the Netherlands. |
Jan Meijer <jan.meijer=>uninett.no> René Klomp <Rene.Klomp=>os3.nl> Edwin Schaap <Edwin.Schaap=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 14 N |
Architecture of dynamic VPNs in OpenFlow.The networking community considers OpenFlow and SDN in general as a possible solution against the ossification of networks. Despite the attention for SDN in the networking community, it is unclear if the SDN architecture is open enough to avoid ossification in itself. So, OpenFlow should be capable of providing current network functions with at least the same level of efficiency. For example, using an OpenFlow network to provide a pseudo-wire to customers, or being able to do use an OpenFlow router as a border router. In this RP, we will analyze the practical implications of SDN architecture compared to one or more of the leading solutions in current networks:
|
Rudolf StrijkersRudolf Strijkers <rudolf.strijkers=>tno.nl> Michiel Appelman <michiel.appelman=>os3.nl> |
R P |
2 |
| 15 F |
Retroactively estimating system clock skew from stored web browser cookies.Timeline analysis plays an important role in forensic examinations. To do this well, one needs to know whether the clock that was used to generate the times- tamps that make up such a timeline was representing the true time on that mo- ment. For a forensic image of a system, retroactively determining the clock skew at the time of artefact creation is a challenge. One way of estimating skew is to analyze HTTP transaction residues. Using the server-generated timestamps (ex- piry information) in HTTP interactions, one can estimate the difference between client and server clocks. However, the existance of many unknowns1 and the intricacies of the HTTP protocol - in particular, the multiple and fundamentally different ways in which expiry information can be transmitted - complicate mat- ters greatly. Without knowledge of the actual HTTP message, heuristics need to be applied to arrive at an estimate. Combining multiple sources of external reference clocks can improve the estimate. Since forensic web artefacts will com- monly be the result of interacting with public web servers, recording the details of the behaviour of those web servers into a database is feasable. Such will allow formalized heuristics based on real-world data. For web servers not recorded in this database and for timespans for which no recordings are available, HTTP parameters might be inferred to varying degrees. Using Bayesian probability theory one can arrive at a calculated measure of the confidence level for skew estimates provided by a particular web artefact analysis. |
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> Marnix Kaart <m.kaart=>nfi.minvenj.nl> Wicher Minnaard <Wicher.Minnaard=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 17 F |
Random Sampling applied to Rapid Disk Analysis.As described in the presentation by Garfinkel (http://cenic2010.cenic.org/program/slides/2010-03-09_CENIC.pdf), random sampling of disk content can be used to determine the complexity of the data on a disk. Was a disk wiped, which part of the disk is empty or what are the chances after find X number of blocks that the disk is empty are some questions that can be given an answer with a certain level of confidence. Can this method also be applied to determine the priority in which a set of disks needs to be analysed? |
Zeno Geradts <zeno=>holmes.nl> Erwin van Eijk <eijk=>holmes.nl> Nicolas Canceill <Nicolas.Canceill=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 18 F |
Reconstructing web pages from browser caches.There are some tools that are able to reconstruct webpages from temporary internet files. Reconstructing these pages can be quite useful. Focus will be to find a generic method given a normalized database to reconstruct webpages. |
Zeno Geradts <zeno=>holmes.nl> Ruud van Baar <baar=>holmes.nl> Edwin Schaap <Edwin.Schaap=>os3.nl> Iwan Hoogendoorn <Iwan.Hoogendoorn=>os3.nl> |
R P |
2 |
| 20 F |
Time skew analysis using web cookies.The accuracy of timestamps has important implications in digital forensics. This paper presents two algorithms for determining the system clock skew by using web cookies in a web browser cache. The first algorithm lists possible time skews in a ranked order while the second algorithm finds different time intervals when the computer's system clock had a certain alteration. The algorithms were implemented and tested on modified web browser caches which simulated the system clock being altered or misconfigured at the time the web browser was used. The first algorithm is able to correctly identify the actual time skew as the one with the highest rank. The second algorithm can identify intervals of time skews but suffers from false positive results. |
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> Marnix Kaart <m.kaart=>nfi.minvenj.nl> Bjorgvin Ragnarsson <Bjorgvin.Ragnarsson=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 22 F |
SSH Botnet Member Credential Collection using Connect Back Honeypots.This is a research proposal for a project that identifies possibilities for actively fighting against SSH Brute force botnets. The theory of the Author is, that SSH-Botnets usually consist of systems, which them-self have been compromised by the same technique and similar word-lists. Research backing up this theory is presented as well a short pre-evaluation of the suggested technique, which indicates possible success of the experiment needed to validate the theory. The experiment and resources needed therefor are then described. An ethical and judicial evaluation then concludes the proposal. |
Jaap van Ginkel <J.A.vanGinkel=>uva.nl>
Tobias Fiebig <tobias.fiebig=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 28 N |
OpenFlow network virtualization with FlowVisor.The OpenFlow [1] protocol is a protocol that places the forwarding logic of a switch to a external Open- Flow controller. These controllers make the for- warding decisions based on the network topology and rule set. OpenFlow is a kind of Software De- fined Networking (SDN) [2].The OpenFlow network topology can be sepa- rated into different slices which act as independent networks. A slice can be any combination of any switch ports, mac-addresses, IP-addresses, applica- tion ports. Each slice has its own view on his part of the network topology. Doing experiments inside one slice does not affect the proper working of other networks slices. So experiments can be done safely inside the production network. As describes in the papers in section 3. One can use FlowVisor [3] to create these virtual networks inside the network topology. FlowVisor is currently considered as a research project. FlowVisor works as transparent proxy between an OpenFlow switch an multiple OpenFlow con- trollers. Incoming switch traffic will be intercept by the FlowVisor en depending on the rules which are configured, the traffic is send to the designated OpenFlow controller. The Openflow controller then makes the forwarding decision and sends it back to the switch. On the way to the switch the FlowVisor will check if the made decision of the OpenFlow controller is allowed and send it to the switch. |
Ronald van der Pol <Ronald.vanderPol=>surfnet.nl> Sebastian Dabkiewicz <sebastian.dabkiewicz=>os3.nl> |
R P |
2 |
| 29 F |
Defending against DNS reflection amplification attacks..The Domain Name System (DNS) is recently seeing more and more reflection amplification attacks, where spoofed UDP packets are bounced off DNS servers to attack a target. DNS is a good amplifier, because it is possible to generate large responses with relatively small queries.Such DDoS attacks become more sophisticated, making it hard for packet filters to catch the traffic. This urges to push the filtering towards the name server, so that the defense mechanisms can also become more sophisticated. What characterizes these attacks, which metrics should be used to be able to successfully block illegal traffic? Current defense mechanisms are already in use. Some attacks are countered with packet filter software, like iptables. Two name server implementations, BIND9 [1] and NSD [2], apply Response Rate Limiting (RRL) techniques. There is a proposal to do DNS Dampening [3], which is based on the theory of BGP Route Dampening. How effective are these solutions? Where do they excel and what are their weaknesses? Can these defense mechanisms be turned into a target itself? |
Matthijs Mekking <matthijs=>nlnetlabs.nl> Thijs Rozekrans <Thijs.Rozekrans=>os3.nl> Javy de Koning <javy.dekoning=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 30 F |
Remote relay attack on RFID access control systems using NFC enabled devices.Contactless smart cards are often used for physical access control. Most RFID access control systems use some sort of challenge-response authentication mechanism. These mechanisms should protect the authentication system against replay attacks, but are still vulnerable to relay attacks.Most of the documented relay attacks are targeted towards the radio/physical layer [1,2]. One attack describes a proof of concept using a device-emulator, which introduces some timing issues [3]. Investigate whether it is feasible to perform such an attack using two NFC enabled smart phones. One phone should act as a reader, while the other should be used as a device-emulator. Construct a proof of concept in which an Internet (3G, Wifi) connection is used to relay the challenge/response between the two phones. Develop a solution to eliminate any timing issues that could occur in such a setup. Some programming skills and experience with smart card protocols are probably required to successfully complete this RP project. |
Bart Roos <bart.roos=>ncsc.nl> Pieter Westein <pieter.westein=>os3.nl> Wouter van Dullink <Wouter.vanDullink=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 31 N |
Discovery and Mapping of the Dutch National Critical IP Infrastructure.Internet has become a critical infrastructure governing our every day lives, just like electricity, gas, drinking water, (surface) water management, telecom (in general), and transport in crisis situations. Thinking of the Internet as a critical infrastructure, one can discern the physical connections of networks and between networks (e.g., the fiber cables), and the logical connections on IP level (thus how Internet traffic crosses networks from source to destination).To anticipate on crisis situations, it can be very insightful to have a notion how government departments and companies that fullfil a role (as a provider or coordinator) in critical infrastructures are connected on IP level. For example, what are the interdependent networks between electricity companies and drinking water facilities. In case of large Internet disturbances, which IP networks must remain available to provide a minimal functionality to ensure continuation of "The Netherlands Ltd". http://www.nlnetlabs.nl/ |
Benno Overeinder <benno=>nlnetlabs.nl> Razvan Oprea <Razvan.Oprea=>os3.nl> Fahimeh Alizadeh <Fahimeh.Alizadeh=>os3.nl> |
R P |
2 |
| 32 N |
Topology discovery.Network topology discovery is the process to automatically generate a network topology by examining the connected devices or messages on the wire. In this task, the students are asked to compare the different methods and protocols available for topology discovery (think: Link Management Protocol, Cisco Discovery Protocol, SDH section traces, Spanning Tree Protocol, OSPF, IS-IS, and traceroute).The students should both classify the protocols and method to hook into these protocols, and recommend a particular topology discovery method based on its distinguishing features. The students should create a small prototype to demonstrate the feasibility of their recommendation. |
Freek Dijkstra <Freek.Dijkstra=>sara.nl> Dennis Pellikaan <dennis.pellikaan=>os3.nl> Diederik Vandevenne <Diederik.Vandevenne=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 34 N |
Detecting and preventing execution of malicious code injected through cookies.Web applications have grown to play a big part in the internet of today. A wide variety of web applications exist, which enable us to do online shopping, work, communicate through fora, chat and social media. The vast majority of the web applications is written in php and runs on the apache webserver. Which makes a platform running apache and php an attractive target for attackers. New detection methods and applications have been developed to counter these attack methods. The applications which try to detect and/or detect these attacks are commonly known as "web application firewalls". In this research the detection and, possible, prevention of a new multi stage attack which uses cookies to transport an encrypted payload will be investigated. |
Gertjan Oude Lohuis <gertjan=>byte.nl> Sudesh Jethoe <Sudesh.Jethoe=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
1 |
| 35 N |
Using wavelengths outside of the Telecom spectrum.It is common practice today to use Wavelength Division Multiplexing, WDM, devices on network links to increase the total amount of bandwidth that a single optical network link can carry. The WDM accomplishes this by assigning each input data stream its own unique light wavelength channel, λ. Not every wave- length is suitable for heavy traffic usage because of the physical characteristics of these channels. Our hypothesis is that these channels could be used for lower speed appli- cations such as monitoring and out of band management.To test our hypothesis we will look at the possibilities of the unused wave- lengths outside of the Telecom spectrum. The main research question will be as follows:
Note that our presentation was made in HTML and JavaScript, so the PDF version only contains the text and pictures of each slide and no proper layout. Our presentation can still be found online (with full, proper, formatting) at http://remydb.github.com/rp1 Also, the source for all our work can be viewed here: https://github.com/remydb/rp1/ This includes the latex source for the report and the python scripts we created for our test setups. |
Erik Radius <erik=>beetlefiberoptics.com> Stefan Plug <stefan.plug=>os3.nl> Remy de Boer <remy.deboer=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
1 |
| 36 N |
GreenSONAR; A multi-domain energy profiling system based on perfSONAR.Can we instrument a tool like perfSONAR (www.perfsonar.net) to monitor energy consumption of network equipment? What are the useful metrics to be stored in the management archive of perfSONAR?perfSONAR is an infrastructure for network performance monitoring, currently used in the European GEANT network and in the Internet2 and ESnet networks in the US. The measurements collected by greenSONAR should allow to determine the current energy profile of an end-to-end paths crossing several domains, and could provide indication on how to 'green' the network by using different network paths. |
Paola Grosso <p.grosso=>uva.nl> Karel van der Veldt <karel.vd.veldt=>uva.nl> Hao Zhu <H.Zhu=>uva.nl> Lutz Engels <lutz.engels=>os3.nl> Todor Yakimov <Todor.Yakimov=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
1 |
| 37 N |
Monitoring GreenClouds; Evaluating the trade-off between Performance and Energy Consumption in DAS-4.The DAS-4 cluster (http://www.cs.vu.nl/das4/) is instrumented with power meters that record the power characteristics of (some of) the nodes.What do the measurements we obtain from our power meters tell us about the energy consumption of the clusters? What could be improved in the data collections mechanisms in order to increase their usability in green scheduling mechanisms? |
Karel van der Veldt <karel.vd.veldt=>uva.nl> Hao Zhu <H.Zhu=>uva.nl> Paola Grosso <p.grosso=>uva.nl> Renato Fontana <Renato.Fontana=>os3.nl> Katerina Mparmpopoulou <katerina.mparmpopoulou=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 39 S F |
SmartTV Hacking.SmartTVs are becoming more mainstream. Smart TVs are TVs with an internet connection to share media in your home network but also install apps from the app-store. The APIs provide means to access shared data on the network using DLNA. Here we see a possibility for new types of malware target home systems.You will start the research with creating an overview of the different Smart TVs, then create a threat landscape of the threats on Smart TVs and then focus on one specific threat and try to develop and exploit a vulnerability. It is up to you to decide the exact direction of the vulnerability. It might be malware in apps, exploit the TV itself using the network, etc. Here one can find 3 youtube movies of expoits as investigated during the RP:
|
Henri Hambartsumyan <HHambartsumyan=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Nikos Sidiropoulos <Nikos.Sidiropoulos=>os3.nl> Periklis Stefopoulos <periklis.stefopoulos=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 40 NS F |
Tinfoil attack; A study on the security threats and weaknesses of GSM-based communication in BMW car.Modern high-end cars can be fitted with wifi hotspots, 3g internet connection, keyless entry and even smartphone apps to remotely control your car. Of course such features introduce new risks. We are interested in the risks and threats of this new features. We will provide a car for testing purposes which will enable you to test the security aspects of these modern features. You are free to choose the area of the car you want to focus on, however, we urge to focus on one specific feature. |
Henri Hambartsumyan <HHambartsumyan=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Thijs Houtenbos <thijs.houtenbos=>os3.nl> Jurgen Kloosterman <jurgen.kloosterman=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 42 S F |
Malware Analysis on Carberp.BotNet / trojan horse system analysis. |
Henri Hambartsumyan <HHambartsumyan=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Wouter Katz <wouter.katz=>os3.nl> Ralph Dolmans <Ralph.Dolmans=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
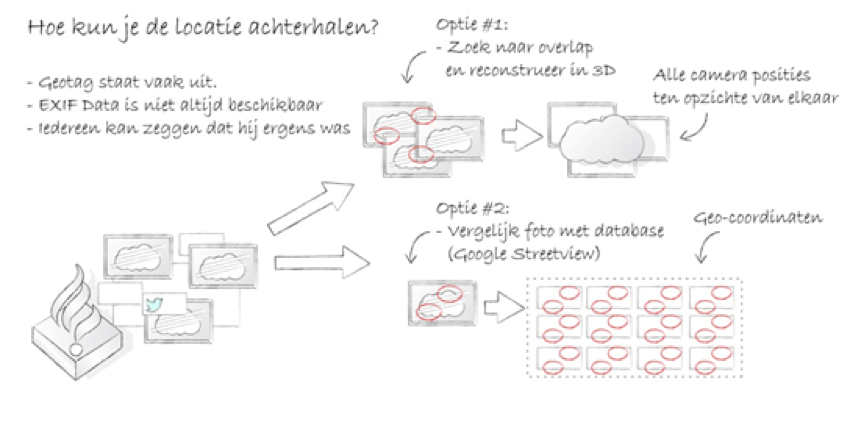
| 45 F |
Image-based localization of pictures using Google Streetview images.Goal:Determine the geographical location where a picture on social media was taken, based on the picture itself. Approach: Develop a concept and make a quickscan of suitable technologies. Validate the concept and chosen technology in a small-scale experiment. (e.g. pictures you have taken yourself matched with Google Streetview using open-source libraries). Result: Presentation of the concept and feasibility study of the chosen technology. |
John Schavemaker <john.schavemaker=>tno.nl> Bas Vlaszaty <Bas.Vlaszaty <Bas Vlaszaty=>os3.nl> Tim Timmermans <Tim.Timmermans=>os3.nl> |
R P |
1 |
| 50 SN |
Load balancing in ESB based service platform.This project will investigate load balancing solutions provided by major existing Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) implementation such as Fuse ESB or Apache ServiceMix, writing and running simple test program and collecting statistics. ESB is a widely adopted SOA platform for Enterprise Information System (EIS).The project will require investigating one of the ESB platforms, e.g. FUSE ESB in particular those that are responsible for load balancing and intelligent message queuing Normalised Message Router and ActiveMQ. Simple load balancing scenario for installation of a few services depending on different message traffic patterns need to be demonstrated. This work will contribute to the on-going project and may be resulted in a joint paper or conference presentation. |
Yuri Demchenko <y.demchenko=>uva.nl> Nick Barendregt <nick.barendregt=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 54 N |
Performance optimisation of webmail.Open source web frontends to mail servers ('webmail') are an often neglected area of development, but over the world hundreds of millions of end users depend on these technologies to have confidential and secure access to their private and business mailboxes. Applications like Horde, Roundcube, SoGo, SquirrelMail and Afterlogic Webmail are well known in the hosting industry. The amount of load these systems can take without losing responsiveness differs significantly, as it depends as much on architectural designs and the quality of the code (e.g. built-in concurrency and threading) as it may on external factors such as DNS performance, disk I/O and even which filesystem is used.The project wants to help better understand how the performance of web mail applications is determined, which is a prerequisite to better tuning these applications to actual usage patterns and design towards a next generation of better solutions. In this project you will create a benchmark suite comprised of various typical email loads for different profiles of users and usage, which can be used together with a tool like postal http://freecode.com/projects/postal to subsequently investigate performance of the various components of webmail solutions for each different types of load. You will profile the different components based on the different usage patterns, providing insight and recommendations into where optimisation effort from the developers should be spent. |
Michiel Leenaars <michiel=>nlnet.nl> Periklis Stefopoulos <periklis.stefopoulos=>os3.nl> Katerina Mparmpopoulou <katerina.mparmpopoulou=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 55 N |
Using PMTUD for a higher DNS responsiveness.Large DNS responses can be too big to pass through a network-path in one piece. Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) would normally help in fragmenting such packets, but it requires state; A sender has to remember what it had sent to be able to resent it fragmented. Current nameservers are all implemented in a stateless way; Once a request has been replied, it is forgotten.With PMTUD in IPv6 however, the signalling packet indicating a packet does not fit (ICMPv6 PTB), carries as much as possible of the original packet.
|
Willem Toorop <Willem=>NLnetLabs.nl> Benno Overeinder <benno=>NLnetLabs.nl> Hanieh Bagheri <hanieh.bagheri=>os3.nl> Victor Boteanu <victor.boteanu=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
1 |
| 56 S |
Additional certificate verification methods for TLS client applications. The idea is to store and check TLS certificates and notify the user about suspicious changes of valid certificates, to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. The Certificate Patrol Firefox extension does something similar, but we want to do this checking on the level of TLS libraries, to be able to use this mechanism with any application using those libraries. We would look into how we can implement this in a feasible way, and develop a proof-of-concept implementation. Also, we would investigate how we can combine this with other protocols for certificate validation, like DANE. |
Michiel Leenaars <michiel=>nlnet.nl> Gabor Toth <Gabor.Toth=>os3.nl> Tjebbe Vlieg <Tjebbe.Vlieg=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
1 |
| 57 |
Minimizing ARP traffic in the AMS-IX switching platform using OpenFlow.The AMS-IX ISP Peering LAN connects more than 600 routers. These routers use ARP in order to establish connectivity with each other. Due to the nature of ARP the growing number of connected routers leads to scalability problems. In order to limit the amount of broadcast traffic AMS-IX operates an ARP Sponge[1]. This tool reduces the amount of broadcast traffic on the Peering LAN by replying to ARP requests for unused addresses.The goal of this research project is to investigate the use of OpenFlow to further bring down the amount of broadcast traffic on the AMS-IX Peering LAN. This project consists of two parts:
|
Martin Pels <martin.pels=>ams-ix.net> Hanieh Bagheri <hanieh.bagheri=>os3.nl> Victor Boteanu <Victor.Boteanu=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 59 N |
BGP origin validation (RPKI).SURFnet is working on routing security and is involved in the development of route origin validation (RPKI).With the first RPKI implementations getting available into production software for routers it is time to think about the way this technology can be used. From measurements we do we noted that there are still a lot of invalid and unknown routes. Research questions on this are;
See for the proof of concept: http://academic.slowpoke.nl/ |
Jac Kloots <Jac.Kloots=>surfnet.nl> Marijke Kaat <Marijke.Kaat=>surfnet.nl> Javy de Koning <Javy.deKoning=>os3.nl> Remy de Boer <remy.deboer=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
|
68
N
|
Reliable Client-Server Connections; Making Telenet secure.With DNSSEC, we finally have reliable DNS information; with DANE, we finally get proper constraints on server certificates, even self-signed ones. It might be interesting to consider publishing CERT records for client-side certificates in DNS as well, but that would publish detailed contact information for domain users, which would be too supportive of spam and scam.Another mechanism that is almost completely possible now, is to store the certificates in LDAP and look it up with uid=someone,dc=example,dc=com through a DNS SRV reference to an LDAP server, and to retrieve a userCertificate. This mechanism could be used by any website that wanted to validate a user's identity or pseudonymity. Anyone adding DNSSEC to this mix would be improving the security level of their service, so it is a good reason to embrace DNSSEC, if DANE wasn't good enough yet. What we are looking for is a sort of TLS-wrapper that fulfills the following functions:
|
Michiel Leenaars <michiel=>nlnet.nl> Rene Klomp <Rene.Klomp=>os3.nl> Thijs Rozekrans <Thijs.Rozekrans=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 70 SF |
Using git to circumvent censorship of access to the Tor network.Tor is a network of encrypted tunnels for people to route their communications through to improve their privacy 1. The traffic is encrypted in as many layers as the number of hops it takes through the Tor network, a technique called onion routing 2. This allows people to use the internet without their network operator knowing where the traffic is going nor the receiver knowing where the traffic is originating from. The only thing passing through Tor relays is encrypted traffic and none of them know both who is the originator and who is the receiver.Some network operators do not allow connections to the Tor network and the original method to implement this policy was to block all IP addresses of Tor relays, which are publicly known. This lead to the introduction of bridge relays, which are unlisted from the Tor relay directory. Bridge relay operators give out information to users about their bridges in hope that the knowledge doesn’t reach the censoring network operators. The next step in the arms-race was deep packet inspection, distinguishing Tor traffic from acceptable traffic. The response from the Tor project was to shape their protocol to look similar to SSL 3. Later, when an operator blocked SSL traffic all together, the Tor project implemented obfuscation of the SSL- looking Tor traffic 4 - which later was also blocked by the same operator. The latest development is Pluggable Transports 5. It is a modular framework for developing different obfuscation methods for users to contact bridge relays without network operators detecting the fact that they are doing so. The main goal of this research is to answer the following questions: Is it possible to shape Tor traffic in such a way that it looks identical to the git protocol? What methods could a censor apply to iden- tify Tor bridge relays communicating with end users using such an obfuscated protocol? In order to answer the research question, we also need to know the following: 1. What methods are used for censoring Tor traffic? 2. How do our methods compare to other attempts at obfuscating Tor traffic? 3. How can the git protocol be detected and fingerprinted? 4. What is the best way to create a mapping between the git and Tor protocols? |
Henri Hambartsumyan <HHambartsumyan=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Bjorgvin Ragnarsson <Bjorgvin.Ragnarsson=>os3.nl> Pieter Westein <pieter.westein=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 74 P |
UvA Data Service: Towards an Unified Architecture for Scientific Data Aggregation.This is not an official RP but a student in the PIRE program with NSF and dr. Paola Grosso. |
Ana Oprescu, Paola Grosso Pedro Bello Maldonado |
||
| 75 N |
OpenFlow Enlightenment; Extending lightpaths through the campus network.OpenFlow has support for adding (push), changing (set) or removing (pop) VLAN and MPLS tags. The goal in the project is to test these features with respect to functionality, performance, limitation, etc. These tests will be done with the pica8 3290 OpenFlow switches in the SURFnet testbed. If these switches support the features in hardware (by the ASIC), the performance will probably be good. But there is probably a limitation in the number of tags that are supported in hardware. When using more tags, it either does not work or it will be handled in software. These limits need to be investigated. After these tests are done a working prototype with these features is to be setup. One possible showcase is to use the tagging features in combination with the lighpath service of SURFnet.Lightpaths are dedicated circuits that are terminated at the campus edge. For universities it is difficult to extend these circuits to the end user. Tagging the traffic with VLAN or MPLS might be a solution to this problem. |
Marijke Kaat <kaat@surfnet.nl> Ronald van der Pol <Ronald.vanderPol=>SURFnet.nl> Diederik Vandevenne <Diederik.Vandevenne=>os3.nl> Tjebbe Vlieg <Tjebbe.Vlieg=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 77 F |
Detecting client-side e-banking fraud using a heuristic model.How to prevent internet banking fraud in a widget driven browser appFor as long as internet banking has existed, criminal organisations have been actively trying to commit fraud leveraging weaknesses in banking applications. Just as long as criminals have been active, banks have been actively preventing this type of fraud from happening. With the introduction of Widget driven applications, using protocols like JSON and REST for data transfer, the world is changing. Also preventative measures have to evolve into a Web 2.0 ready controls potentially leveraging other and new mechanisms for detecting and preventing fraud. This assignment will entail research into possibilities for fraud detection in a Web 2.0 driven internet banking application to, then, set the requirements for Widget development and build a detection framework to enhance current controls and push fraud detection to the next level. |
Steven Raspe <steven.raspe=>nl.abnamro.com> Mark Wiggerman <mark.wiggerman=>nl.abnamro.com> Jurgen Kloosterman <jurgen.kloosterman=>os3.nl> Tim Timmermans <tim.timmerman=>=>os3.nl |
R
P |
2 |
|
88
N
|
Design of a Social Messaging System Using Stateful Multicast.GNUnet is a framework for secure peer-to-peer networking. Multicast packet delivery is current being developed for it, along with messaging functionality provided by PSYC (Protocol for SYnchronous Conferencing). The longer term goal is to develop a multicast messaging system using the combination of the two.A preliminary implementation of the PSYC component exists that provides basic messaging functionality, but it needs more work and better integration into the GNUnet framework. This project aims to improve this situation by identifying integration points and defining the APIs necessary for the multicast messaging functionality to be realized, and used by client applications. This involves considering aspects including:
|
Christian Grothoff <grothoff=>in.tum.de> Gabor Toth < Gabor.Toth=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 90 |
A visual analytics approach to network security hygiene.There is a lot of public information on security threats and issues emanating from networks. For example, SPAM and botnet blacklists. There has been some research into potentially malicious networks, based on such information. However, policy makers, security officers and other stakeholders find difficulties in getting an overview and gaining insight.Research questions:
|
Martijn van der Heide <mheide=>kpn-cert.nl> Tarik El Yassem <Tarik.ElYassem=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 91 F |
Automated vulnerability scanning and exploitation.There is a lot of attention being given to vulnerabilities in popular content management systems such as Joomla and Wordpress. These vulnerabilities are often being used to compromise web servers, to initiate DoS attacks or to spread malware using drive-by attacks. With most of the attention aimed towards these popular scripts, there is a huge amount of potential vulnerable script code out there being unnoticed. Sites such as hotscript.com have more than 17.000 PHP scripts available for download. It is likely that this codebase contains a lot of vulnerable code.The research question for this RP exists of three sub questions.
|
"Jop van der Lelie (NCSC-NL)" <jop.vanderlelie=>ncsc.nl> Bart Roos <bart.roos=>ncsc.nl> Thijs Houtenbos <thijs.houtenbos=>os3.nl> Dennis Pellikaan <dennis.pellikaan=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 92 F |
Identifying Patterns in DNS Traffic.The Domain Name System has recently been abused to perform the biggest Denial of Service attack in the history of the Internet. By using open resolvers and some authoritative server, the attack pushed 300 Gigabits of traffic every second towards the target. While (it is theorized) the attacker only needed several Gigabits to accomplish this attack.The goal of this Research Project is to identify the characteristics of DNS amplification attacks from the authoritative server?s and resolver?s perspective. Surfnet has agreed to share data from their DNS servers to be analyzed. Using Visual Analytics techniques, the 'bad' packet(streams) are identified to create more effective blocking of these attacks. |
Marcel Worring <m.worring=>uva.nl> Matthijs Mekking <matthijs=>nlnetlabs.nl> Pieter Lexis <pieter.lexis=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 94 F |
Forensic DHCP Information Extraction from Home Routers.The rising distribution of high speed end user connections leads to an increasing amount of small routing devices in end users homes. These - mostly linux based - devices tend to hold their DHCP lease files in memory.This data is of huge interest from a forensics perspective. This research will identify the obtainability and volatility of those DHCP lease files which hold information on when which MAC address has been seen in an end users network. |
Andreas Schuster <a.schuster=>yendor.net> Tobias Fiebig <tobias.fiebig=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 95 F |
Metasploit-able honeypots.Most honeypots implement outdated vulnerabilities, which gives a skewed vision on threat detection and assessment. In this project, a method will be developed to automatically detect patterns in a subset of the Metasploit framework exploits by analyzing the traffic as the exploits are being executed against a target system. Next, these patterns will be converted to scripts for honeypots, with the goal to allow honeypots to pose as Metasploit-able computers.With Metasploit being the framework of choice for penetration testing, emulating a large number of vulnerabilities in a honeypot that the publically available exploits in Metasploit abuse, will give security researchers a more up-to-date and broader insight on attacker activities. |
Jop van der Lelie <Jop.vanderLelie=>ncsc.nl> Bart Roos <Bart.Roos=>ncsc.nl> Wouter Katz <wouter.katz=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
| 96 F |
Preventing DNS Amplification Attacks using white- and greylisting.DNS amplification attacks cause big problems. On resolver DNS servers these attacks can be prevented by closing the servers, preventing it on authoritative DNS servers is more difficult. Previous research showed that the current techniques developed to mitigate these attacks (e.g. RRL and DNS dampening) are not sufficient. BCP38 can solve the problem but is not widely deployed.The purpose of this project is to research the possibility of implementing a black- or whitelisting mechanism on authoritative DNS servers, containing DNS resolvers that are in a BCP38 compliant network. This way it might be possible to put pressure on ISPs to implement BCP38 and rate limit or block malicious networks. |
Maurits van der Schee <m.vanderschee@ocom.com> Ralph Dolmans <Ralph.Dolmans=>os3.nl> |
R
P |
2 |
Presentations-rp2
The event is stretched over two days: Wednesday-Thursday July 3-4 th, 2013.System and Network related projects:
| Wednesday July 3 th, 2013. Auditorium C 0.005 at Science Park 904 NL-1098 XH Amsterdam. | ||||
| Time | #RP | Title | Name(s) | RP |
| 09h30 | # | Welcome, introduction. | Cees de Laat | RP |
| 09h30 | 4 | Linux Open Source Distributed Filesystem. | Remco van Vugt | 1 |
| 09h55 | 88 | GNUnet and PSYC integration. | Gabor Toth | 2 |
| 10h20 | 19 | SaaS Gatekeeper. | Sudesh Jethoe | 2 |
| 10h45 | break | |||
| 11h00 | 31 | Discovery and Mapping of the Dutch National Critical IP Infrastructure. | Razvan Oprea, Fahimeh Alizadeh | 2 |
| 11h30 | 54 | Performance optimisation of webmail. | Periklis Stefopoulos, Katerina Mparmpopoulou | 2 |
| 12h00 | 57 | OpenFlow at AMS-IX. | Hanieh Bagheri, Victor Boteanu | 2 |
| 12h30 | Lunch | |||
| 13h15 | 59 | BGP route origin validation. | Javy de Koning, Remy de Boer | 2 |
| 13h45 | 68 | Reliable Client-Server Connections. | Rene Klomp, Thijs Rozekrans | 2 |
| 14h15 | 75 | Extending lightpaths to end users in a generic, dynamic and secure way. | Diederik Vandevenne, Tjebbe Vlieg | 2 |
| 14h45 | break | |||
| 15h00 | 14 | Architecture of dynamic VPNs in OpenFlow. | Michiel Appelman | 2 |
| 15h25 | 89 | Mice and Elephants. | Ioannis Giannoulatos | 1 |
| 15h50 | 74 | UvA Data Service: Towards an Unified Architecture for Scientific Data Aggregation. | Pedro Bello Maldonado | |
| 16h15 | Closing. | Cees de Laat & OS3 team | ||
| 16h20 | End |
|||
Forensics related projects:
| Thursday July 4 th, 2013, room C 0.005 at Science Park 904 NL-1098 XH Amsterdam. | ||||
| Time | #RP | Title | Name(s) | RP |
| 09h45 | # | Welcome, introduction. | Cees de Laat | RP |
| 09h50 | 17 | Using random sampling as a way to determine disk complexity. | Nicolas Canceill | 1 |
| 10h15 | 92 | Analysis of DNS amplification attack packets. | Pieter Lexis | 2 |
| 10h45 | break | |||
| 11h00 | 18 | Research cache rebuilding for different browsers. | Iwan Hoogendoorn, Edwin Schaap | 2 |
| 11h30 | 70 | Using git to circumvent censorship of access to the Tor network. | Bjorgvin Ragnarsson, Pieter Westein | 2 |
| 12h00 | 77 | Detection of client-side e-banking fraud using a heuristic model. | Jurgen Kloosterman, Tim Timmermans | 2 |
| 12h30 | Lunch | |||
| 13h15 | 90 | Gaining insight into network hygiene a visual analytics approach. | Tarik El Yassem | 2 |
| 13h40 | 91 | Automated vulnerability scanning and exploitation. | Thijs Houtenbos, Dennis Pellikaan | 2 |
| 14h10 | 94 | Forensic DHCP Information Extraction from Home Routers. | Tobias Fiebig | 2 |
| 14h35 | break | |||
| 14h50 | 95 | Metasploit-able honeypots. | Wouter Katz | 2 |
| 15h15 | 96 | DNS Whitelisting. | Ralph Dolmans | 2 |
| 15h40 | Closing. | Cees de Laat & OS3 team | ||
| Drinks & etc. in OS3 lab! | Team et al. | |||
Presentations-rp1
| Wednesday feb 6th in room B1.23 at Science Park 904 NL-1098XH Amsterdam. | |||||
| Time | #RP | Title | Name(s) | T | RP |
| 9h30 | Welcome, introduction. | Cees de Laat | |||
| 9h40 | 42 | Malware Analysis. | Wouter Katz, Ralph Dolmans | SF | 1 |
| 10h00 | 40 | Car Security. | Thijs Houtenbos, Jurgen Kloosterman | SNF | 1 |
| 10h20 | break | ||||
| 10h40 | 56 | Additional certificate verification methods for TLS client applications. | Gabor Toth, Tjebbe Vlieg | S | 1 |
| 11h00 | 57 | Extending a service delivery platform from a consumers perspective. | Sudesh Jethoe | SN | 2 |
| 11h20 | 8 | FileSender Terabyte Challenge. | René Klomp, Edwin Schaap | N | 1 |
| 11h40 | Evaluation. | Cees de Laat & OS3 team | |||
| 11h50 | End | ||||
| Friday feb 8th in room B1.23 at Science Park 904 NL-1098XH Amsterdam. | |||||
| Time | #RP | Title | Name(s) | T | RP |
| 9h30 | Welcome, introduction. | Cees de Laat | |||
| 9h40 | 53 | Migration models for hosting companies. | Pawel Oljasz, Michal Mioduszewski | SN | 1 |
| 10h00 | 4 | Transparent DDOS filtering. | Nicolas Canceill, Ioannis Giannoulatos | SN | 1 |
| 10h20 | 37 | Monitoring GreenClouds. | Renato Fontana, Katerina Mparmpopoulou | N | 1 |
| 10h40 | 5 | break | |||
| 11h00 | 20 | Digital trace database for Bayesian analysis. | Bjorgvin Ragnarsson, Wicher Minnaard | F | 1 |
| 11h20 | 22 | SSH Botnet Member Credential Collection using Connect Back Honeypots. | Tobias Fiebig | F | 1 |
| 11h40 | 30 | Remote relay attack on RFID access control systems using NFC enabled devices. | Pieter Westein, Wouter van Dullink | F | 1 |
| 12h00 | Lunch | ||||
| 13h00 | 32 | Topology discovery. | Dennis Pellikaan, Diederik Vandevenne | N | 1 |
| 13h20 | 45 | Image-based localization of social media pictures. | Bas Vlaszaty, Tim Timmermans | F | 1 |
| 13h40 | 39 | SmartTV Hacking. | Nikos Sidiropoulos, Periklis Stefopoulos | SF | 1 |
| 14h00 | break | ||||
| 14h20 | 36 | GreenSONAR. | Lutz Engels, Todor Yakimov | N | 1 |
| 14h40 | 35 | Using wavelengths outside of the Telecom spectrum. | Stefan Plug, Remy de Boer | N | 1 |
| 15h00 | 14 | Moving SNE to the Cloud. | Yudha AgungPribadi, Jos van Dijk | SN | 1 |
| 15h20 | break | ||||
| 15h40 | 3 | Traffic Volume vs. Network Inspection. | Fahimeh Alizadeh, Rawi Ramdhan | SN | 1 |
| 16h00 | 29 | Defending against DNS reflection amplification attacks. | Thijs Rozekrans, Javy de Koning | F | 1 |
| 16h20 | 55 | Big Data DNS. | Hanieh Bagheri, Victor Boteanu | N | 1 |
| 16h40 | 57 | Extending a service delivery platform from a consumers perspective. | Sudesh Jethoe | N | 2 |
| 17h00 | Evaluation. | Cees de Laat & OS3 team | |||
| 17h10 | End | ||||
Auxillary presentations of RP's ouside normal schedule:
| Date/Time | #RP | Title | Name(s) | T | RP |
| dec 2012 | 28 | OpenFlow network virtualization with FlowVisor. | Sebastian Dabkiewicz | N | 2 |