LeftOver projects 2011 - 2012

| # |
title summary |
supervisor contact students |
R P |
1 / 2 |
| 1 SN |
Virtualization vs. Security Boundaries.Traditionally, security defenses are built upon a classification of the sensitivity and criticality of data and services. This leads to a logical layering into zones, with an emphasis on command and control at the point of inter-zone traffic. The classical "defense in depth" approach applies a series of defensive measures applied to network traffic as it traverses the various layers.Virtualization erodes the natural edges, and this affects guarding system and network boundaries. In turn, additional technology is developed to add instruments to virtual infrastructure. The question that arises is the validity of this approach in terms of fitness for purpose, maintainability, scalability and practical viability. |
Jeroen Scheerder <Jeroen.Scheerder=>on2it.net> |
R P |
|
| 2 SN |
DNS security revisited.The crucial DNS remains a liability today. In the past, several attempts - and huge government impulses - have been made towards DNSsec adaptation. Success has been far from evident, meriting a closer look. At this point, there might be actual field data to (dis)prove DNSsec skepticism. DNSsec support has been mandatory for several TLDs now for an extensive period. While mandatory, participation has been less than complete. And of the zones for which DNSsec was deployed, it's an open question whether this initial deployment has been followed by proper maintenance (as is necessary for DNSsec zones).Specific questions are: What adaptation rate has DNSsec seen amongst (for example) .gov zones? What is the trend, and the adaptation timeline? Of the zones offering DNSsec at point in time T, which ones are still valid at point T+n? Running hypothesis would that DNSsec has been plausibly tried, and has been proven a failure. Let's see this hypothesis disproved! Or… else…? |
Jeroen Scheerder <Jeroen.Scheerder=>on2it.net> |
R P |
|
| 3 SN |
Traffic Volume vs. Network Inspection.Traffic volume remains ever-increasing. Peak throughput at AMSIX for example saw a yearly increase from 0.8T to 1.2T roughly (sep 2010 vs. sep 2011). Yet simultaneously growing needs to deal with increasingly evasive network applications, increasingly strenuous compliance regulations, and high-profile malware activity (Mariposa, Conficker, STUXnet, …) has given rise to powerful real-time inspection technology.An important question is if it is possible, and if so how, to bring and keep inspection capacity close to full network capacity, even in the face of continuous strong growth. |
Jeroen Scheerder <Jeroen.Scheerder=>on2it.net> |
R P |
|
| 5 SN |
Monitoring the cloud.The main challenge when migrating services to the cloud is to identify the security issues and the problems which can derive from loss of control. After the services are migrated to a cloud provider, organizations should continue monitoring these services. Most of the cloud providers already have some type of monitoring which allows clients to see the status of their services, but unfortunately sometimes these monitoring tools are not detailed enough or the mapping between the virtual and physical resources isn't visualized correctly.This project consists of a literature study and the design and implementation of a real-time monitoring tool. The literature study should examine how different virtualization techniques and architecture designs can influence the client's services. This is followed by the implementation of a reliable monitoring tool which shows the mapping of the client's services to the underlying virtualized and physical layers. The status and performance of these services should be monitored near real-time. |
Tunde Balint <balint.tunde=>kpmg.nl> |
R P |
|
| 7 S |
Tiled video streaming implementation.P.S. these are way more software engineering, but if someone fabricates a relevant research question for SNE RP1 out of these, please contact me (CdL)Build a native (C, CUDA) implementation of tiled video streaming. This is an overhaul of the current proof of concept within the European FP7 Fascinate project. The implementation will be used in user pilots. Contact: Omar Niamut <omar.niamut=>tno.nl>Native tiled video streaming on iPhone, iPad or AndroidSummary: Build an app (Objective-C or Java) that can read and play tiled videos on a smartphone or tablet. The main challenge here lies in synchronizing multiple videos on a per-frame level. Contact: Omar Niamut <omar.niamut=>tno.nl>Second-screen synchronisationSummary: Build a synchronised solution that lets subtitles run on an iPad simultaneously with a streaming TV broadcast. The synchronization solution should be network-based, e.g. using the RTCP protocol extensions for inter-destination media synchronization, as being developed in the FP7 HBB-Next project.Contact: Ray van Brandenburg <ray.vanbrandenburg=>tno.nl> Social TV marking of scenesSummary: Build a social-TV solution where one person can draw a highlight on a TV broadcast, which can be seen by his friends in real time.Contact: Oskar van Deventer <oskar.vandeventer=>tno.nl> |
Omar Niamut <omar.niamut=>tno.nl> |
R P |
|
| 10 S |
Data Integrity in Digital Archives.Investigate techniques to improve the reliability of the archiving facilities at SARA and tools for implenting and increasing regular data integrity checks.Context: SARA operates two multi petabyte digital archive facilities. These facilities are based on a tiering storage model with an online disk tier and a nearline tape based tier. Data is automatically policy based migrated between tiers. The archiving software stack is based on SGI DMF (Data Migration Facillity). DMF uses internally checksums to guard data integrity. These are not available outside the system. Research: Investigate techniques for improving integrity of the archive facilities at SARA and develop demonstration tools fo better and regular data integrity checks. |
Ans Sullot <Ans=>sara.nl> |
R P |
|
| 11 SF |
Security Metrics.Onsight Solutions delivers network security and application delivery solutions to middle sized and large companies. Onsight believes that offering just the security hardware does not add any security. Managing this hardware in a proper way does. Offering support or full management of those devices is the core business of Onsight.But how can you measure security (or maybe you measure the change a hacker is able to attack your environment ?) What factors are important when you try to grade the security solution at a company. And can those factors be monitored in an automated way 24x7? What tools are required? Or maybe some human resources? When it becomes possible to define a number, and compare this with a certain level (which might be a standard or a contracted value), it becomes possible to monitor the security solution. In case the security level drops, an engineer gets alarmed to take some action. So the level of security is maintained. Beside this, a number for security is easy to understand for people who have to decide about the budget, but don't know anything about IT security (think about the IT managers/Security officers). Main question: "How can you assign a number to the quality of a security solution at a company?". Some subquestions: What parameters are important to measure? And what is the importance of each factor? What tools are required to measure this? For example you can think about honeypots, port scans, vulnerability scans, etc. And maybe some external data sources are required, to gather security information? |
Roel van der Jagt <roel.van.der.jagt=>onsight.nl> |
R P |
|
| 12 N |
OpenNSA.Currently we are participating in the development of a protocol for inter-domain circuit provisioning. One of the implementations is OpenNSA, an open-source implementation by NorduNet. This research project is to look at both the current capabilities of this software project, compare with other implementations, and examine the applicability of OpenNSA (or others) to the machines in our testbed network.This will allow us to quickly and automatically make connections across the globe and do network tests, or other resource sharing experiments. |
Jeroen van der Ham <vdham=>uva.nl> |
R P |
|
| 15 SF |
Security scanner for mobile apps.The current Apple App Store and Android Market contain thousands of apps, and many more are added every day. More and more companies are creating apps that provide some service to their customers from their mobile phone. The security of these apps is varying and we have seen in the past that all kinds of security issues with the apps come to light. A short selection of these security issues are clear text storing of passwords, insecure data transmission of critical data, (illegal?) harvesting and transmitting of data from different parts of the phone outside the app's domain. As with many other software components, it is becoming clear that apps need to be tested for security issues before going live. We want students to think and create a way to do this security scanning of apps less error prone and more automated. Testing may include black box and white box.Steps in the research can include: 1. Provide a framework of insecurities that these mobile apps should be checked for (e.g. way of storing credentials, network communication) 2. Create an easy-to-setup testing environment that can be used for the security testing of the mobile apps. This should be usable for apps downloadable from the Store/Market and for apps provided separately. Research at KPMG IT Advisory can be challenging. We strive for the best results and therefore invest a considerable amount of time in you, to help you achieve the best. But to succeed together we require fully determined students that would like to go the extra mile. The RP topics as stated on the website are fixed but we are open to changes in the exact research approach if the student prefers. We encouraged students to come up with own ideas and approaches. During the short intake interview your are invited to bring your ideas and approaches to the table. We use the intake to select the students who will get the opportunity to perform their research project at KPMG. |
Marc Smeets <smeets.marc=>kpmg.nl> |
R P |
|
| 16 SF |
Content Security Protection.Some time ago Mozilla designed a new web standard called CSP (Content Security Protection, see https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/CSP). W3C has taken Mozilla's work and has a public working draft at https://dvcs.w3.org/hg/content-security-policy/raw-file/tip/csp-specification.dev.html The goal of CSP is to separate data (html) from executable code (JavaScript).Students are asked to research the CSP standard as it is known now and: 1. Review this standard, try to identify gaps/omissions also looking at Mozilla's implementation and knowing the history of the separation of code and data (compare this development to No Execute bits/DEP); 2. One of the following, or both if time allows:
The RP topics as stated on the website are fixed but we are open to changes in the exact research approach if the student prefers. We encouraged students to come up with own ideas and approaches. During the short intake interview your are invited to bring your ideas and approaches to the table. We use the intake to select the students who will get the opportunity to perform their research project at KPMG. |
Marc Smeets <smeets.marc=>kpmg.nl> |
R P |
|
| 17 SF |
Feasibility of attacks on weak SSL ciphers.Weak SSL ciphers have been around since many years. In theory many ciphers are cracked. But in current networks we find that the usage of weak ciphers is still very common. In practice only a few attempts have been successful, with EFF’s FPGA attack on DES with COPACOBANA being a noteworthy one. Many other ‘theoretically cracked’ weak ciphers are still not easy to crack in practice.We would like the students to research the feasibility of cracking weak ciphers used. The research can include the entire process from intercepting communication, extracting the data used for attack, select best way of cracking, perform crack and uncover the secrets. Ideally, the research results in a statement on the feasibility of cracking these weak ciphers. What ciphers exactly to be included will be selected at the start of the research. Research at KPMG IT Advisory can be challenging. We strive for the best results and therefore invest a considerable amount of time in you, to help you achieve the best. But to succeed together we require fully determined students that would like to go the extra mile. The RP topics as stated on the website are fixed but we are open to changes in the exact research approach if the student prefers. We encouraged students to come up with own ideas and approaches. During the short intake interview your are invited to bring your ideas and approaches to the table. We use the intake to select the students who will get the opportunity to perform their research project at KPMG. |
Marc Smeets <smeets.marc=>kpmg.nl> |
R P |
|
| 27 N |
IPV6 risks and vulnerabilities.Because the world starts to adopt IPv6 more and more we also run into the security problems involved with this migration/adaptation. Of course IPv6 has built-in security, compliance with IPSec is mandatory in IPv6, and IPSec is actually a part of the IPv6 protocol. IPv6 provides header extensions that ease the implementation of encryption, authentication, and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). IPSec functionality is basically identical in IPv6 and IPv4, but one benefit of IPv6 is that IPSec can be utilized along the entire route, from source to destination. But it can be assumed that only enforcing the use of IPSec within IPv6 isn't solving all security problems and therefore there is a need to research to see what the vulnerabilities and risks are during the use of IPv6. For this research project the focus is on the vulnerabilities that exist because of the lack of using secure techniques and protocols in combination with IPv6. |
R.F.Visser <rene.visser=>govcert.nl> |
R P |
|
| 28 F |
Determining camera model from JPEG quantization tables.Acceleration methods for searching image databases, for example through optimizing search through quantization tables in JPEG. Some investigation has been done on how this JPEG characteristic can be used by such methods, but further investigation should give a better view on its feasibility. Other JPEG characteristics not yet exploited by any search method in current use may be investigated as well. These methods are used to search for images that have, for example, deviant or specific values for these characteristics. Certain values may indicate the use of a camera of some kind, or that it has been altered (or recreated) by specific image editing software. A proof-of-concept that shows the use of such characteristics in search methods will probably be implemented.Netherlands Forensics Institute. |
Marcel Worring <m.worring=>uva.nl> Zeno Geradts <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
R P |
|
| 31 SN |
Moving SNE to the Cloud.The cloud is these days often considered as a valuable resource to gain competitive advantage to businesses. It's clear advantages like improved scalability, agility and cost efficiency can make it an obvious choice for certain businesses to move to such an environment. Although there might be some issues concerning bandwidth, security and regulations, it is also becoming a more and more considered (and sometimes already used) option for educational environments. Although these migrations mostly concern commodity services like e-mail and storage, in some universities virtualized applications and desktops are also offered.For this research we would like to make an evaluation of running not the commodity services but the more advanced services provided by the "System and Network Engineering" (SNE) education on a cloud infrastructure. This is mainly composed of providing the students with an environment which enables them to:
|
Jaap van Ginkel <J.A.vanGinkel=>uva.nl> |
R P |
|
| 32 F |
Search strategy recognition.The NFI developed a forensic analysis system (XIRAF) that supports investigators in finding traces in digital material. During the last year, we collected the queries executed by investigators. We ask the student to:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 33 F |
XIRAF Web GUI effectiveness.The NFI developed a forensic analysis system (XIRAF) that supports investigators in finding traces in digital material via a Web interface. During the last year several hundred users used the interface for investigation. The Web GUI is developed by technicians rather than GUI developers. We ask the student to:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 34 F |
XIRAF Case impact.The NFI developed a forensic analysis system (XIRAF) that supports investigators in finding traces in digital material. During the last year XIRAF is used for digital investigation in over 100 cases. We ask the student to:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 36 F |
Efficient K-nearest-neighbours search in high-dimensional spaces.PhotoDNA   is a technology that calculates a unique characteristic for a graphical image. Transformations of the image, e.g. scaling, blurring or changing colors, impact the DNA. However, since the characteristic is a high-dimensional vector, the distance between transformed images is shorter than the distance between completely different images. Also, images that are taken in the same setting have a short distance. The NFI is currently developing a mechanism to apply this technique to case data that is seized for an investigation. For this, a responsive algorithm has to be selected (and implemented) that supports at least the following:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 37 F |
Hot-block replication in distributed storage.When developing a distributed storage, some blocks of the data that are stored on a distributed storage are read more often than other blocks. Since these hot blocks are needed more often, they preferable have a higher availability, meaning that more copies of them occur in the distributed storage. We ask the student to:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 38 F |
Digital trace database for Bayesian analysis.The NFI is currently introducing Bayesian analysis in digital forensics. To use calculated Bayesian conclusions, we need to set up databases with digital traces that give insight in the current state. We ask the student to:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 39 F |
Multi-dimensional query strategies in key-value stores.The NFI developed a forensic analysis system (XIRAF) that supports investigators in finding traces in digital material. The system currently makes use of an internal Data Model that is mapped to a SQL table structure. The queries that can be performed on the data are very flexible, resulting in many joins and nestings. Currently, we are researching if we can store the data in a distributed (noSQL) database. For that, the data model needs to be remapped. We ask the student to:
|
Zeno Geradts (DT) <zeno=>holmes.nl> |
||
| 42 NF |
Mobile Application Security.Because company users are more and more dependent on their mobile devices, the applications on these devices also contain more and more company related information. In cooperation with the students we would like to research some interesting application a bit more in depth. What applications are sending information in clear text, what flaws are there etc.An example case is WhatsApp messenger: WhatsApp sends all the messages in clear text. When connected to a public hotspot, these messages can be intercepted. So you might ask yourself the question:
|
Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Derk Wieringa <DWieringa=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> |
||
| 44 SNF |
Access Control Assessment.Organisations deal with many different applications, databases and operating systems. Often the application, database and operating system have a separate access control mechanisms with their own login credentials. Within organisations that frequently deal with high employee turnover this can raise issues regarding the consistency of access rights.This research project focusses on setting up an Access Control assessment that can clearly present the problems of access control. Using reporting tools we would like to build a Proof of Concept for the Access Control assessment. |
Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Derk Wieringa <DWieringa=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> |
||
| 45 NF |
Decrypting GSM Traffic.What is the risk of using GSM?How fast do we have to switch, now that it is possible to create a decryption station. Based on the published information during the most recent CCC event we would like to challenge the students to create a POC that can be used to decrypt the A5/1 encryption protocol that's used by various telco's in the Netherlands (and other countries) to encrypt the GSM traffic. |
Coen Steenbeek <CSteenbeek=>deloitte.nl> Derk Wieringa <DWieringa=>deloitte.nl> Martijn Knuiman <MKnuiman=>deloitte.nl> |
R P |
|
| 48 N |
Optical paths in DAS-4.The SNE group is installing an optical cross connect (DAS-4 switch) that will allow to create path on demands between four locations on the DAS-4 cluster. Dynamic paths between clusters can improve applications performance and contribute to a more energy conscious use of equipment. The student will evaluate the current code used to control the switch and modify and improve it if needed. He will define and configure a control and monitoring system for the switch using webservices. He will identify the most useful topology setup in relation to existing and foreseen applications. Finally the student will identify the steps to integrate the switch in the OpenNSA fabric.Knowledge of Python and LabView is required Ref; http://www.cs.vu.nl/das4/research.shtml Ref; http://www.surfnet.nl/nl/Innovatieprogramma%27s/gigaport3/Documents/GP3-2010-PHO-8R-Gamage-GovBrd.pdf Ref: https://bitbucket.org/myzt/das4_pxc/ |
Ralph Koning <R.Koning=>uva.nl> Paola Grosso <p.grosso=>uva.nl> |
||
| 49 SN |
Automatic services composition in GEMBus/ESB based Cloud PaaS platform.This project will investigate Cloud Platform as a Service (PaaS) implementation based on GEMBus (GEANT Multidomain Bus) and ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) and look for solutions to automatically compose and deploy services. ESB is a widely adopted SOA platform for Enterprise Information System (EIS) and GEMBus is ESB extension for distributed multi-domain services.The project will require investigating one of the ESB platforms, e.g. FUSE ESB, and finding which functional and configuration components need to be added to the ESB platform to support automated services composition and dynamic configuration. Simple services composition scenario and prototype need to be demonstrated. This work will contribute to the on-going project and may be resulted in a joint paper or conference presentation. |
Yuri Demchenko <y.demchenko=>uva.nl> |
||
| 50 SN |
Load balancing in ESB based service platform.This project will investigate load balancing solutions provided by major existing Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) implementation such as Fuse ESB or Apache ServiceMix, writing and running simple test program and collecting statistics. ESB is a widely adopted SOA platform for Enterprise Information System (EIS).The project will require investigating one of the ESB platforms, e.g. FUSE ESB in particular those that are responsible for load balancing and intelligent message queuing Normalised Message Router and ActiveMQ. Simple load balancing scenario for installation of a few services depending on different message traffic patterns need to be demonstrated. This work will contribute to the on-going project and may be resulted in a joint paper or conference presentation. |
Yuri Demchenko <y.demchenko=>uva.nl> |
||
| 51 N |
OpenFlow.OpenFlow is a new networking technology that is getting a lot of attention lately. It is a form of software defined networking where forwarding and control plane are separated and applications can program the forwarding tables. OpenFlow developments are moving very quickly and therefore it is difficult to define the details ofa project at this time. Therefore, the exact details of this project will be discussed in June. A suitable project will be defined with input by Cees, Ronald and the students. Area's of interest include a.o. interoperability testing, performance testing, multi-tenancy (e.g. flowvisor) and monitoring. |
Ronald van der Pol <rvdp=>sara.nl> Cees de Laat <delaat=>uva.nl> |
||
| 52 N |
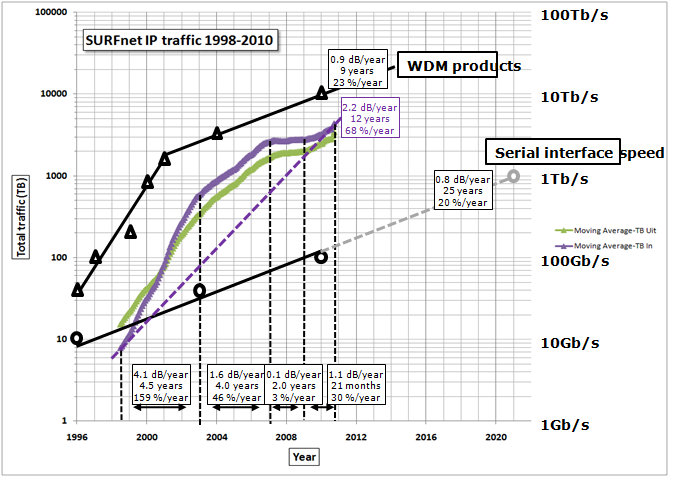
Analysis of IP Traffic Volume at SURFnet. |
Roeland Nuijts <roeland.nuijts=>surfnet.nl> |
||
| 55 F |
Security DataNose system.The DataNose system is in use at the UvA-FNWI to organize different aspects of education. The system contains schedule and management information about courses, exercises, etc. This rp is about the security of that online system. Students are asked to proof-hack the system to expose weak spots. |
gerrit Oomens <G.Oomens@uva.nl> |
||
| 56 N |
Requirements and design of a routing tools library and API.With router configuration of large networks and Internet exchanges like AMS-IX or LINX, a number of tools are available. The de facto standard tool is IRRToolSet, which is complex and hard to use. Other toolsets implement a partial implementation of parts of the standard that are (most) frequently used.In this project the student can choose for a breadth or depth approach. For the breadth approach, the student can compare the usage of the current toolsets, and consult e.g. engineers at AMS-IX to define requirements and an API for such a routing toolset. A depth approach makes a trade-off between a complete API design versus the implementation of some basic functionality to interface with Internet Routing Registries. The project results can include a rudimentary but modular and extensible library that can be used for future development of a full-fledged routing toolset. http://www.nlnetlabs.nl/ |
Benno Overeinder <benno=>nlnetlabs.nl> |
||
| 58 |
Topology discovery.Network topology discovery is the process to automatically generate a network topology by examining the connected devices or messages on the wire. In this task, the students are asked to compare the different methods and protocols available for topology discovery (think: Link Management Protocol, Cisco Discovery Protocol, SDH section traces, Spanning Tree Protocol, OSPF, IS-IS, and traceroute).The students should both classify the protocols and method to hook into these protocols, and recommend a particular topology discovery method based on its distinguishing features. The students should create a small prototype to demonstrate the feasibility of their recommendation. |
Freek Dijkstra <Freek.Dijkstra=>sara.nl> |
||
| 59 SN |
Live IT Infrastructure Requirements Verification.ContextThe environment for the research project is the Information Services organization of Air France- KLM. In this organization the datacenter is responsible for the management of the business applications and the underlying system and network infrastructure. The applications management department of the datacenter has defined a concept called The Artificial IT Intervention Handler (AITIH). This concept is realized as an AGILE/Scrum project. One of the functions in this concept is a Blueprint Generator. A Blueprint is a graphical representation of infrastructure components of the system and network infrastructure showing servers and its connectivity to the LAN and SAN network. IST situation of the IT infrastructure Auto discovery information is collected every day by system and network monitoring tools. This information shows the actual status of the IT infrastructure. This information is stored in a database for analysis. Blueprints can be generated from this database using a proprietary tool based on SVG. SOLL situation of the IT infrastructure IT architects are involved in the development and change process of business applications. They are responsible for the IT Global Design (ITGD) of the underlying infrastructure for the business applications. An ITGD is part of the documentation of a business application. IT architects define the principles that should be used when designing a particular application infrastructure. Research question Business applications have non-functional requirements for the infrastructure. The ITGD defines the non-functional requirements. Availability is the most important infrastructure requirement for business applications. The research questions are:
|
Betty Gommans <betty.gommans2=>klm.com> |